Introduction: Why SAP FICO Configuration Matters
Every successful organization relies on accurate financial management. In SAP, this is achieved through SAP FICO Configuration, the process of setting up the Financial Accounting (FI) and Controlling (CO) modules. This guide will help you understand the essentials of configuration, from General Ledger to Asset Accounting, making it easier to manage business finance.
👉 If you’re new to SAP, think of this as your FICO configuration guide — practical, structured, and designed to avoid common mistakes.
What is SAP FICO Configuration?
SAP FICO Configuration involves setting up structures that allow businesses to record, process, and report financial transactions. It ensures compliance with accounting standards while providing transparency for decision-making.
In simpler terms, it’s the financial backbone of SAP. Without proper setup, reporting errors, compliance issues, and audit problems can arise.
🔗 For official references, check the SAP Help Portal.
Key Components of SAP FI-CO Setup
Here are the major areas covered in SAP financial setup:
- Company Code – Defines the smallest organizational unit for external reporting.
- Chart of Accounts – Master list of GL accounts used for reporting.
- General Ledger (GL) – Central repository for all accounting transactions.
- Accounts Payable & Receivable – Configuration for vendor and customer transactions.
- Asset Accounting (AA) – Tracks company assets like equipment and property.
- Controlling (CO) – Internal reporting for cost centers, profit centers, and budgets.
Step-by-Step FICO Configuration Guide
1. Company Code Setup
- Define a company code (e.g., BR77).
- Assign local currency, fiscal year variant, and country-specific settings.
2. Chart of Accounts
- Create a standard chart of accounts.
- Assign it to the company code.
- Configure account groups and number ranges.
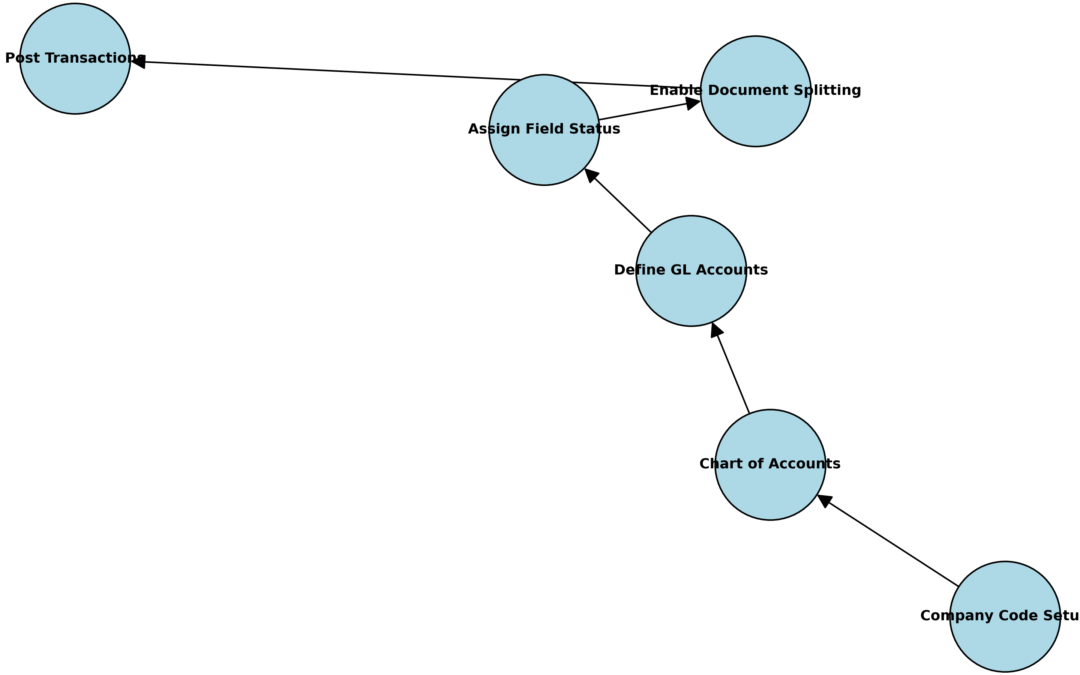
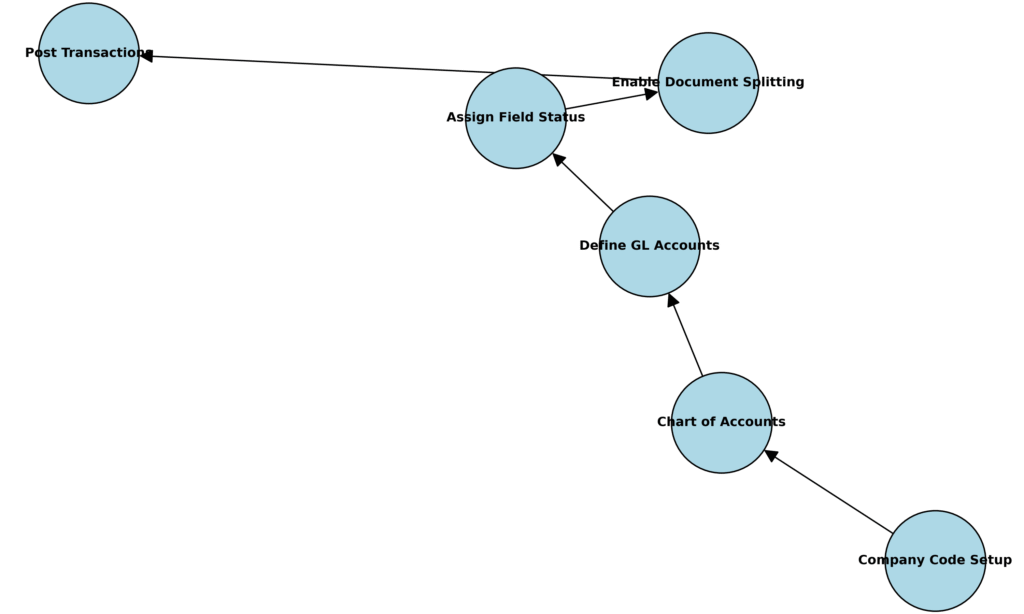
3. General Ledger (GL)
- Define GL accounts for assets, liabilities, revenues, and expenses.
- Assign field status variants.
- Enable document splitting if required.
📊 Diagram: SAP FICO Configuration — GL Setup Flow
Alt text: SAP FICO General Ledger configuration flowchart.
4. Accounts Payable & Receivable
- Vendor master data setup.
- Customer master data setup.
- Automatic payment program configuration.
5. Asset Accounting (AA)
- Define chart of depreciation.
- Assign depreciation areas.
- Configure asset classes and number ranges.
📊 Diagram: SAP Asset Accounting Configuration Flow
Alt text: SAP Asset Accounting setup process flowchart.
6. Controlling (CO)
- Define controlling area.
- Assign cost elements and cost centers.
- Link CO with FI for reconciliation.
Common Challenges in SAP FICO Configuration & Solutions
- Incorrect Chart of Accounts Mapping → Double-check assignments.
- Fiscal Year Variant Issues → Align with business calendar.
- GL Imbalances → Use trial postings before go-live.
- Asset Accounting Errors → Test depreciation runs in sandbox first.
👉 Want to see practical troubleshooting tips? Check our SAP FICO Training Blog. (Internal link)
Why Proper Configuration is Critical
- Ensures regulatory compliance
- Provides real-time financial reporting
- Reduces audit risks
- Enables data consistency across business units
In short, a strong SAP FI-CO setup helps businesses stay both compliant and competitive.
Conclusion
Mastering SAP FICO Configuration is essential for every finance professional working with SAP. From setting up the company code to configuring asset accounting, each step lays the foundation for reliable reporting and smooth operations.
If you’d like expert-led guidance, explore our SAP FICO Training & Placement Programs.